Which of the following statements about markets is most accurate? This question sparks a captivating inquiry into the intricate world of markets, where supply and demand intertwine to shape economic outcomes. Join us as we embark on a journey to unravel the most precise description of markets, delving into their functions, structures, forces, and equilibrium.
Markets serve as platforms for the exchange of goods and services, facilitating transactions that fuel economic growth. They play a crucial role in determining prices, ensuring efficient allocation of resources, and fostering competition among businesses. Understanding the dynamics of markets is essential for businesses, consumers, and policymakers alike.
Market Definition
Markets are economic systems that facilitate the exchange of goods and services between buyers and sellers. They provide a platform for individuals, businesses, and organizations to engage in transactions, enabling the distribution and allocation of resources within an economy.
There are various types of markets, each characterized by its unique features and mechanisms. These include physical markets, where buyers and sellers interact face-to-face, and virtual markets, such as online marketplaces and e-commerce platforms, which allow for remote transactions.
Key characteristics of markets include the presence of buyers and sellers, the exchange of goods or services, and the establishment of prices through the interaction of supply and demand.
Market Functions: Which Of The Following Statements About Markets Is Most Accurate

Markets perform several primary functions within an economy:
- Facilitation of Exchange:Markets provide a structured environment for buyers and sellers to interact, enabling the exchange of goods and services.
- Price Determination:Through the interaction of supply and demand, markets determine the prices of goods and services, reflecting their relative scarcity and value.
- Resource Allocation:Markets allocate resources efficiently by directing them towards areas of greatest demand and highest value.
- Economic Efficiency:Competitive markets promote economic efficiency by encouraging innovation, reducing costs, and maximizing consumer surplus.
Market Structures

Market structures refer to the different organizational forms and levels of competition that exist within markets. The main types of market structures include:
- Perfect Competition:A market structure characterized by numerous buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, and low barriers to entry and exit.
- Monopoly:A market structure in which a single seller controls a significant share of the market, leading to market power and the ability to set prices above marginal cost.
- Oligopoly:A market structure with a small number of large firms that dominate the market and engage in strategic interactions.
- Monopolistic Competition:A market structure with numerous sellers offering differentiated products and facing some degree of competition.
Market structure significantly impacts competition and market outcomes.
Market Forces
Market forces are factors that influence the behavior of markets and market participants. These forces include:
- Demand:The quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price.
- Supply:The quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to offer for sale at a given price.
- Price:The monetary value at which goods and services are exchanged.
- Competition:The rivalry among sellers to attract customers and increase market share.
Market forces interact to determine market outcomes, such as prices, quantities, and the allocation of resources.
Market Equilibrium

Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity of a good or service supplied equals the quantity demanded. At this point, there is no tendency for prices or quantities to change.
Factors that can shift market equilibrium include changes in demand, supply, or government policies.
Market equilibrium is crucial for market stability and efficient resource allocation.
Market Failure
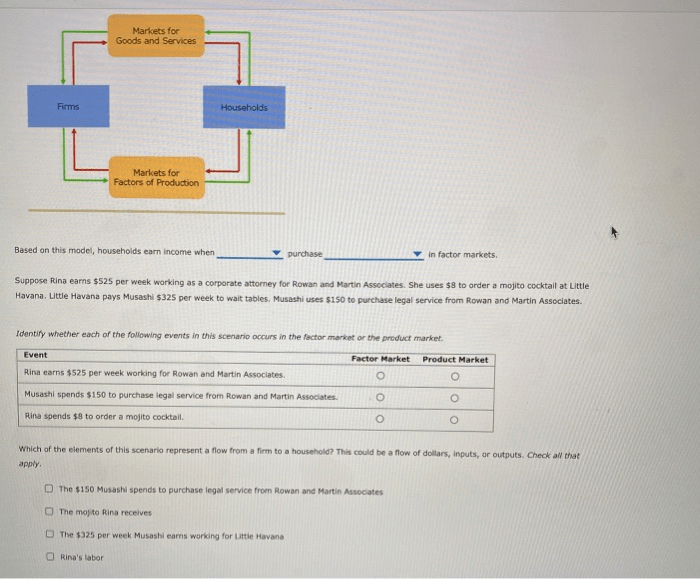
Market failure occurs when markets fail to allocate resources efficiently or achieve socially desirable outcomes. Types of market failures include:
- Externalities:Costs or benefits that affect third parties not directly involved in the market transaction.
- Public Goods:Goods or services that are non-excludable and non-rivalrous, leading to underprovision by the market.
- Monopoly Power:The ability of a single seller to restrict output and raise prices above competitive levels.
- Information Asymmetry:When one party in a transaction has more information than the other, leading to inefficient outcomes.
Market failures can result in economic inefficiency, reduced consumer welfare, and social problems.
Popular Questions
What is the primary function of markets?
Markets facilitate the exchange of goods and services, enabling buyers and sellers to connect and transact.
How do markets determine prices?
Prices in markets are determined by the interaction of supply and demand, with equilibrium prices balancing the quantities supplied and demanded.
What are the different types of market structures?
Common market structures include perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly, and monopolistic competition, each with distinct characteristics and levels of competition.